Introduction: Unraveling the Complexity of Lupus
Lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, presents a complex challenge for both patients and medical professionals alike. Characterized by the immune system attacking healthy tissues, lupus can affect various organs, leading to symptoms ranging from joint pain and fatigue to kidney dysfunction and skin rashes.
Despite advances in treatment, managing lupus remains a significant medical hurdle. However, amidst this challenge, a beacon of hope emerges from the realm of stem cell research.
Stem cell therapy, with its potential to regenerate damaged tissues and modulate immune responses, holds promise as a groundbreaking approach to treating lupus. Let's delve deeper into this exciting frontier in the quest for effective lupus treatment.
Understanding Stem Cells: Nature's Building Blocks
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to develop into various cell types in the body. They serve as the foundation for tissue repair, regeneration, and maintenance.
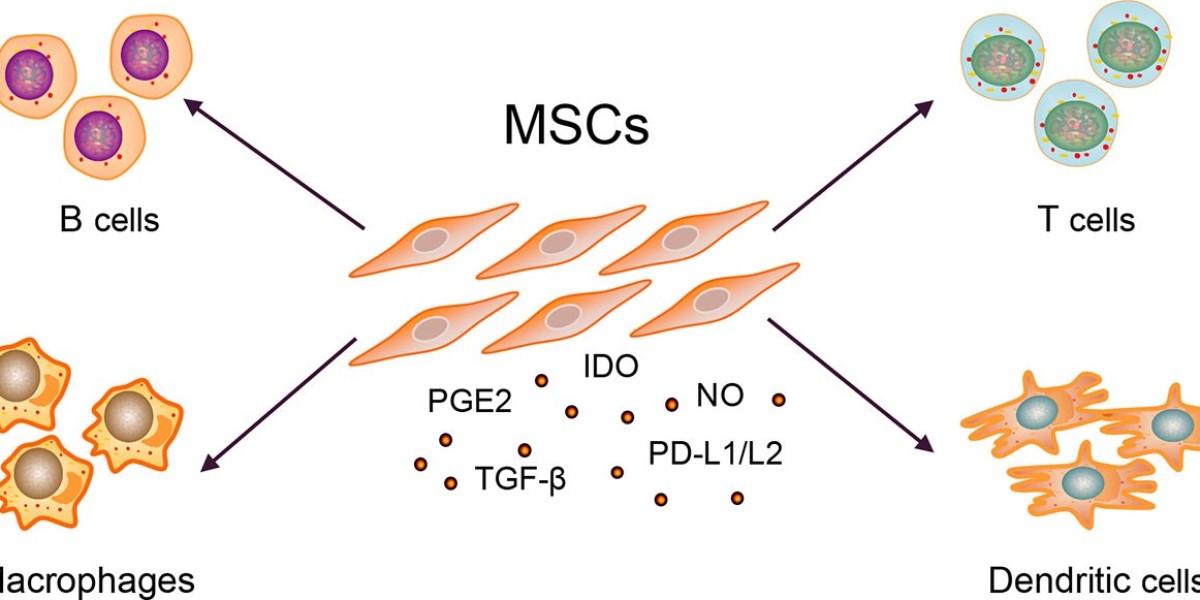
Stem cells can be sourced from different locations, including embryos, bone marrow, and adipose tissue. In the context of lupus treatment, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are of particular interest due to their immunomodulatory properties and their potential to suppress abnormal immune responses.
The Promise of Stem Cell Therapy in Lupus Treatment
Stem cell therapy offers a multifaceted approach to tackling lupus. By harnessing the regenerative and immunomodulatory capabilities of stem cells, researchers aim to address the underlying mechanisms driving the disease while promoting tissue repair and regeneration.
MSCs, in particular, have shown promise in preclinical studies and early-phase clinical trials for lupus treatment.
Regulating the Immune System: Modulating Lupus Flares
One of the hallmarks of lupus is the dysregulation of the immune system, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Stem cell therapy seeks to restore immune balance by suppressing the hyperactive immune responses characteristic of lupus.
MSCs have been shown to exert immunomodulatory effects by inhibiting the proliferation of inflammatory cells and promoting the generation of regulatory immune cells. This immunoregulatory function holds potential for mitigating lupus flares and reducing disease activity.
Promoting Tissue Repair: Addressing Organ Damage
Beyond immune modulation, stem cell therapy offers the possibility of repairing and regenerating damaged tissues in lupus-affected organs. Whether it's the kidneys, skin, joints, or other affected tissues, the regenerative properties of stem cells hold promise for reversing the structural damage caused by lupus.
Clinical studies exploring the use of stem cells in repairing renal damage in lupus nephritis, for example, have shown encouraging results, highlighting the potential of stem cell therapy as a transformative approach to managing organ involvement in lupus.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Road Ahead
While the potential of stem cell therapy in lupus treatment is undeniable, several challenges remain on the path to clinical implementation. Safety concerns, optimal dosing, long-term efficacy, and standardization of protocols are among the key considerations that researchers must address.
Additionally, the heterogeneity of lupus presents a complex landscape, necessitating personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual patient needs. Despite these challenges, ongoing research efforts continue to drive progress in stem cell-based therapies for lupus, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Conclusion: A New Dawn for Lupus Treatment
In conclusion, stem cell therapy represents a promising frontier in the quest for effective lupus treatment. By harnessing the regenerative and immunomodulatory properties of stem cells, researchers are forging new paths towards managing this complex autoimmune disease.
While challenges remain, the potential of stem cell therapy to modulate immune responses, promote tissue repair, and improve outcomes for lupus patients is a beacon of hope in the medical landscape.
As research advances and clinical trials progress, the intersection of stem cells and lupus treatment holds the promise of a brighter future for those living with this challenging condition.